Design that feels as good as it looks.
Introduction: Why People Confuse UI and UX
In the digital age, businesses increasingly focus on delivering exceptional user experiences, yet many still confuse UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience). While UI shapes the visual look and feel of a product, UX ensures it works intuitively and meaningfully. Understanding the difference between them is crucial for building successful digital products. A strong combination of UI and UX can improve engagement, conversions, and long-term brand trust. To explore more about the impact of user experience in business success, check out Nielsen Norman Group’s detailed insights on UX best practices.
The Rise of Design-Centric Thinking
As technology evolved, design became a central part of product development. Terms like UI (User Interface) and UX (User Experience) gained popularity, often being used interchangeably. Yet, while both aim to improve digital experiences, their roles differ greatly. UI focuses on how something looks; UX focuses on how it works and feels. This confusion arises because the best digital products seamlessly merge both disciplines.
Common Misconceptions Between UI and UX
One common misconception is that UI is just about visuals and UX is merely about usability. In truth, UI and UX overlap in shaping how users interact and feel. A beautiful interface without thoughtful experience design can frustrate users, while a great UX with poor UI may fail to attract engagement. Understanding their distinct roles helps teams create more balanced, user-centered products.
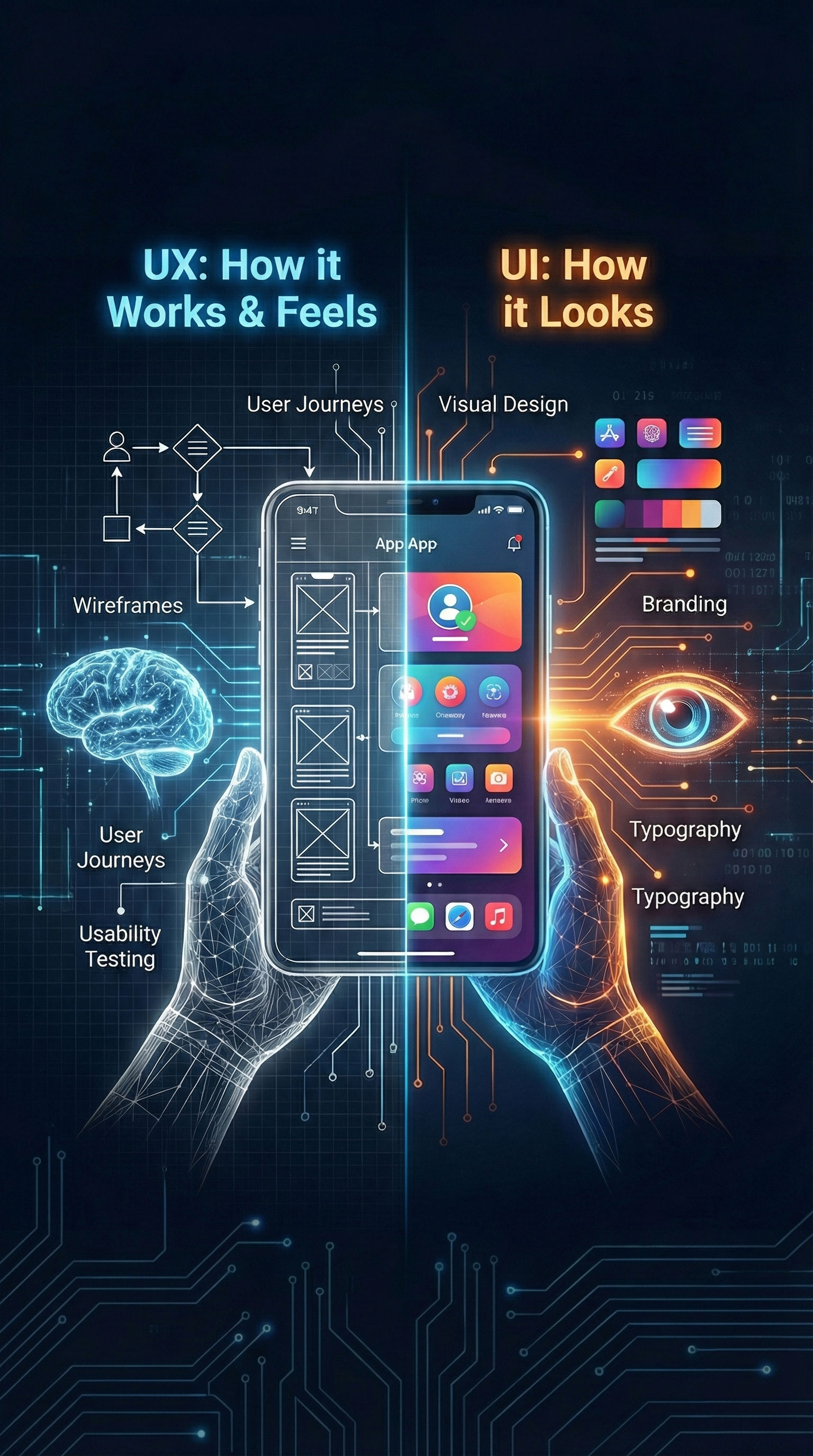
What Is UI (User Interface)?
UI, or User Interface, refers to the visual elements users interact with when engaging with a digital product. This includes everything from buttons and icons to typography, color palettes, and layout structures. A well-designed UI not only captures attention but also reinforces brand identity and usability. Designers focus on creating intuitive, visually appealing systems that allow users to complete actions effortlessly. If you’re interested in learning how leading brands master UI consistency, explore the Google Material Design Guidelines for practical insights.
Visual Elements That Shape Interaction
UI encompasses every visual component users interact with — from buttons and icons to typography and color schemes. It defines the first impression of a product. Good UI guides the eye, builds brand recognition, and ensures accessibility for all users.
The Role of Aesthetics and Branding in UI
Aesthetics play a key role in UI design, influencing how users emotionally connect with a brand. Consistent visual identity, color harmony, and intuitive layouts create trust and recognition. UI bridges visual storytelling with usability, ensuring design decisions align with brand personality.
Key Principles of Good UI Design
Clarity, consistency, and responsiveness are the pillars of effective UI design. A well-designed interface helps users perform actions effortlessly, regardless of device or platform. Designers must consider hierarchy, feedback mechanisms, and accessibility to build inclusive, user-friendly interfaces.
What Is UX (User Experience)?
User Experience (UX) focuses on the overall interaction users have with a product or service. It involves understanding their needs, emotions, and motivations throughout the journey. UX design combines research, usability testing, and data-driven insights to optimize satisfaction and reduce friction. The goal is to create meaningful and memorable experiences that improve customer retention and loyalty. For more on creating effective user journeys, refer to the Interaction Design Foundation’s guide on UX design.
How Users Feel and Flow Through a Product
UX is about how users navigate and experience a product. It focuses on the overall journey — from first impression to goal completion. A well-crafted UX ensures that interactions feel smooth, logical, and rewarding, reducing friction at every step.
UX Research, Wireframes, and Prototyping
Good UX starts with understanding users through research, surveys, and usability tests. Designers map out user flows, create wireframes, and develop prototypes to test ideas before full implementation. This iterative approach minimizes risks and maximizes satisfaction.
Measuring User Satisfaction and Usability
UX success is measured through usability metrics like task completion rate, error frequency, and satisfaction surveys. Continuous improvement based on real feedback helps designers create experiences that evolve with user needs and market trends.
UI vs UX: Understanding the Core Differences
While UI and UX often overlap, their functions and goals differ. UI deals with how a product looks; UX focuses on how it feels and functions. Understanding these distinctions allows teams to design more efficiently and deliver superior products. Both disciplines depend on each other — one cannot succeed without the other. To further explore UI vs UX concepts, visit Adobe’s comparison guide on UI and UX design differences.
Design vs Experience
UI focuses on visuals; UX focuses on feelings. UI answers “How does it look?” while UX asks “How does it feel and work?” Both must align for a product to succeed. UI without UX is decoration; UX without UI is structure without life.
Static vs Dynamic Interaction
UI represents static elements — what users see. UX represents dynamic interactions — how users engage. Together, they define how intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable a product becomes.
The Overlap Between UI and UX in Real Projects
In real-world projects, UI and UX constantly interact. UX research informs design choices, while UI visualizes those insights. Teams that collaborate across both domains deliver cohesive, memorable digital experiences.
Which Matters More for Your Product?
The importance of UI or UX depends on your product’s purpose and target audience. A visually driven brand may rely heavily on UI, while a data-heavy platform prioritizes UX. However, true success comes from balancing both. Businesses that integrate UI and UX design achieve stronger customer engagement and retention. For detailed business insights, check out HubSpot’s article on why UI and UX matter for growth.
When UI Takes the Lead
UI becomes crucial when aesthetics drive user engagement — for example, in fashion or lifestyle apps. Strong visuals enhance emotional appeal, helping brands differentiate in crowded markets.
When UX Defines Success
UX leads when usability and efficiency determine success — such as in financial tools or B2B dashboards. A frictionless experience keeps users loyal and reduces churn.
Finding the Right Balance for Business Goals
The best products balance UI’s appeal with UX’s function. Aligning both with business objectives ensures sustainable growth and brand credibility.
Real-World Examples of UI and UX in Harmony
Leading companies like Apple, Airbnb, and Spotify demonstrate how UI and UX integration defines modern success. Each brand blends aesthetic appeal with intuitive functionality to deliver seamless user experiences. Studying these examples helps designers understand how emotional and practical design coexist. To explore similar studies, review Smashing Magazine’s UI/UX case studies.
Case Study: Apple vs Android
Apple’s ecosystem exemplifies harmony between UI and UX — seamless visuals meet fluid usability. Android, meanwhile, prioritizes flexibility and personalization, offering strong UX variety across brands. Both approaches show how balance can be achieved differently.
How Airbnb Integrates UX Research Into UI Design
Airbnb’s interface reflects years of UX research. Every layout, color, and micro-interaction is informed by real user data, making the UI beautiful and purpose-driven.
How UI and UX Work Together in the Design Process
In a complete design cycle, UI and UX work hand in hand. UX sets the foundation through research and structure, while UI adds visual clarity and emotion. Continuous collaboration between designers, developers, and business teams ensures a cohesive and scalable design system. For comprehensive workflow strategies, explore Figma’s guide on collaborative UI/UX design.
The Iterative Loop of Testing and Improvement
UI and UX design operate in cycles of testing, feedback, and refinement. Each iteration enhances usability and visual harmony, ensuring products evolve with user expectations.
Collaboration Between Designers, Developers, and Stakeholders
A successful design process requires collaboration. Designers craft user flows and visuals, developers ensure technical feasibility, and stakeholders align outcomes with goals — all working together for a seamless experience.
Conclusion: Beyond the UI vs UX Debate
UI and UX are not competitors but collaborators in design. When both disciplines align, products achieve emotional depth and functional excellence. Great digital experiences are the result of balanced visual design and empathetic usability. For additional learning, check out Coursera’s certification programs in UI/UX design fundamentals.
Why Great Products Need Both
UI and UX are two sides of the same coin. Focusing on one without the other limits potential. When balanced, they create digital experiences that are both functional and emotionally engaging.
Building Emotion, Trust, and Functionality Together
The future of design lies in unity — where beauty meets usability. Great products don’t just look good; they feel intuitive, reliable, and human. This harmony between UI and UX defines lasting success in digital design.
Let’s keep in touch.
Discover more about high-performance web design. Follow us on Twitter and Instagram.